
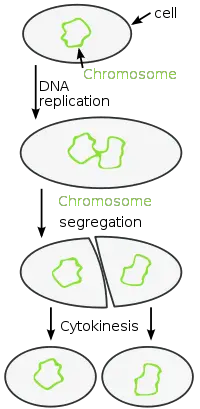
Transduction occurs as a consequence of the actions of bacteriophages, which can transfer small pieces of DNA from one bacteria to another during the course of infecting them. In transformation, prokaryotes pick up small pieces of DNA that other prokaryotes have shed into the environment. The three methods are transformation, transduction and conjugation. Over time, natural selection has pressured these organisms to develop ways to exchange bits of DNA with other organisms to introduce some genetic diversity. Genetic Diversity in EukaryotesĮukaryotes can suffer from a lack of genetic diversity due to asexual reproduction via binary fission. Finally, a cleavage furrow develops in the cell membrane and the two individual cells separate from each other. During this time, the organism increases in size to prepare for division. The DNA uncoils, duplicates and is pulled to opposite poles in the bacterium in an energy-dependent process. Process of Binary Fissionīinary fission has steps that are similar to mitosis (see Mitosis section below). Oblique binary fission is used by organisms in the genus Ceratium (marine dinoflagellates) where the separation occurs obliquely or on a slant. LongitudinalĮuglenas use longitudinal binary fission where the division occurs along its longitudinal plane. Paramecia can switch back and forth the between asexual and sexual reproduction as well. Slime molds can also use sexual reproduction when necessary, such as to create more genetic diversity in a new environment. Some types of slime molds can have more than one fission simultaneously and divide into several daughter cells. In this method, the division happens along the organisms’ transverse axis. Paramecia and planarians (slime molds) use transverse binary fission. Simple binary fission is used by amoebas and can happen along any plane in the organism. There are four main types of binary fission based on where the organism divides itself. coli cells can divide about every 20 minutes. It doesn’t require finding a mate like in sexual reproduction and it is a faster way to reproduce than sexual reproduction.
#Define binary fission plus#
Plus some bacteria could be harmful (such as pathogens ) and would complicate the results of experiments when testing the efficiency of antibiotics or other anti-microbial compounds.Binary fission is the process by which a single-celled organism creates an exact copy of itself.
If a specific bacterium is going to be cultured or grown, other contaminating bacteria would compete for nutrients in the broth or agar. Bacteria can be spread onto the plates, and allowed to form individual colonies of the specific bacterium. These must include: carbohydrates for energy, nitrogen for protein synthesis, plus other minerals.Īgar plates are created by pouring hot molten agar into sterile Petri dishes, which are then allowed to set. Nutrient broth solution or culture medium, allows a liquid or gel to provide all the nutrients needed for bacteria to grow successfully.

There are many ways to culture bacteria, and these include: This level of replication will depend on the availability of nutrients and other suitable conditions such as temperature. Bacterial growth in cultures Bacterial growthīacteria can replicate approximately every 20 minutes by binary fission, which is a simple form of cell division.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
