

We say these values are approximately equal because some voltage is dropped across the winding resistance (R W) of the coil. In this case, the signal source is coupled directly to the load via the inductor, and V RL = E.
#PARALLEL NOTCH FILTER DESIGNER SERIES#
Therefore, the bandwidth of a series LC bandpass filter can be found as: The center frequency of an LC bandpass filter equals the resonant frequency of the circuit. The relationship between these filter characteristics is given as:
#PARALLEL NOTCH FILTER DESIGNER HOW TO#
In section 1, you were shown how to calculate the bandwidth of a bandpass filter when the center frequency (f 0) and filter quality (Q) are known. We will address the effects of loading on filter Q later in this section. It should be noted that the addition of a resistive load o a series or parallel LC filter reduces the Q of the circuit. Note that the higher the Q of the component, the closer it comes to the ideal of Z=X L. As a result, the total opposition to current (Z) presented by the inductor would equal X L. The ideal inductor would have a winding resistance (R W) of 0Ω. Where R W = the winding resistance of the coil. The Q of an inductor is a measure of how close the component comes to the ideal inductor, found as: Even though the two circuits operate differently, they produce the same overall frequency response. Note that the frequency response curve for the circuit in Figure 5 is nearly identical to the one shown in Figure 4. As f in continues to increase, X C approaches 0Ω, which shorts out the load. When the input frequency rises above f r, X C decreases. In this case, the circuit is resistive in nature and the phase angle is 0 o. As a result, the filter is effectively removed from the circuit and V RL ≡ E. When the circuit is operating at resonance, I L = I C and X P approaches infinity. Here is how the parallel LC circuit responds to frequencies above, below, and at resonance. Note that X P and X C, as indicated by the equation.įigure 6: Shunt LC Bandpass Filter Circuit A shunt LC bandpass filter is shown in Figure 6, along with its reactive equivalent circuit. Once you understand the operation of the series LC band pass filter, the operation of its shunt counterpart is relatively easy to visualize. The curve in Figure 5 illustrates the frequency of response of a series LC bandpass filter.įigure 5: Frequency Response Curve of an LC Bandpass Filter Shunt LC Band Pass Filters When f in approaches infinity, X L and X S approach infinity and I T = 0A.
As f in continues to increase, X S increases in magnitude and the impedance phase angle becomes more positive. As a result, the net reactance is inductive in nature and the impedance phase angle is positive. When the input frequency rises above f r, X c decreases and X L increases. The circuit resistive in nature and the phase angle is 0 o. This means that ignoring R W, the circuit current is determined by the source voltage and the load (I T = E/R L).
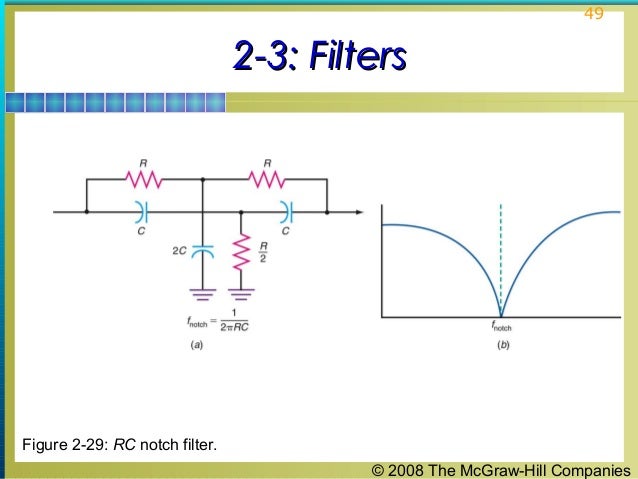
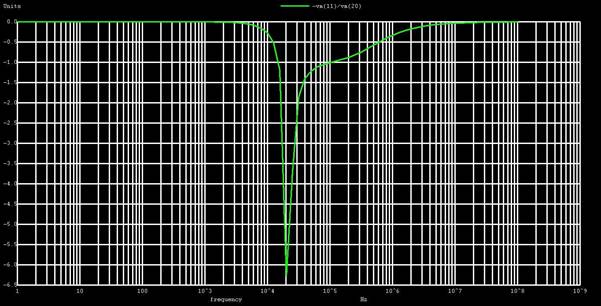
The operation of a series LC bandpass filter is based on the relationship between its input frequency and resonant frequency, as follows: In this circuit, the net series reactance (X S) of the filer is represented as a series component between the source and the load. The operation of a series LC bandpass filter is easiest to understand when the filter represented as an equivalent circuit like the one in Figure 4b.įigure 4: Series LC Bandpass Filter Circuit The basic characteristics of series and parallel resonant circuits are listed in Figure 3.įigure 3: characteristics of series and parallel resonant circuits Series LC Band Pass Filter In each case, the filtering action is based on the resonant characteristics of the LC circuits.įigure 2: LC bandpass and band-stop filters Circuits The circuits in Figure 2b are notch filters. The circuits in Figure 2a are bandpass filters. Most common bandpass ad notch filters are LC filters, like those shown in Figure 2. There are many possible approaches to building bandpass and notch filters. Figure 1: bandpass and band-stop filter frequency response


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
